Introducing the Fact Behind Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane: Advantages, Uses, and Processing Techniques Described
The difference in between sugar beet and sugar cane is often overlooked in discussions about sugar production. Each crop provides one-of-a-kind benefits and applications in numerous markets. Their growing methods and handling methods likewise vary notably. Comprehending these nuances is essential for stakeholders in the sugar market. What ramifications do these distinctions have for wellness, taste, and environmental effect? Exploring these aspects can reveal deeper insights into the worldwide sugar market.

Introduction of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane
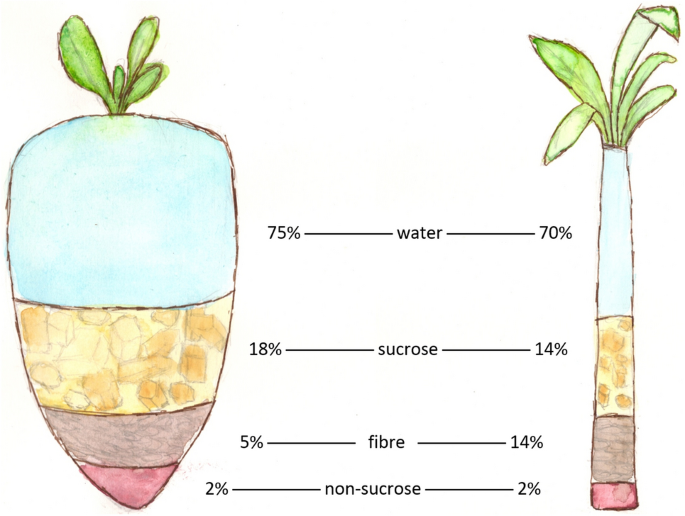
Sugar beet and sugar cane are 2 key resources of sugar, each with unique qualities and farming methods. Sugar beet, an origin veggie, thrives in pleasant environments and is normally harvested in the loss. Its high sugar material, varying from 15% to 20%, makes it a useful plant for sugar manufacturing. The process entails removing juice from the beets, which is after that improved right into granulated sugar.
On the other hand, sugar cane is an exotic lawn that prospers in cozy, moist settings. It can achieve a sugar content of up to 14%, but its tall, coarse stalks call for considerable handling. The cane is crushed to extract juice, which undertakes boiling and condensation to create sugar. Both resources add considerably to the international sugar supply, with sugar beet primarily cultivated in Europe and North America, while sugar cane is mainly expanded in Brazil, India, and other tropical regions.
Farming Practices: Sugar Beet vs. Sugar Cane
Growing techniques for sugar beet and sugar cane vary significantly due to their unique expanding conditions. Sugar beetroots grow in cooler environments with well-drained soil, while sugar cane likes warmer temperature levels and plentiful dampness. Additionally, the harvesting techniques utilized for each and every crop reflect these environmental requirements and influence general yield and top quality.
Expanding Conditions Comparison
While both sugar beet and sugar cane thrive in specific environmental problems, their cultivation methods differ significantly. Sugar beet is largely grown in warm regions, preferring cooler climates with well-drained soil and modest rains. It requires a growing period of about 90 to 120 days, with optimal temperatures between 15 ° C to 25 ° C. In contrast, sugar cane flourishes in exotic and subtropical environments, flourishing in warm temperatures ranging from 20 ° C to 32 ° C. It requires abundant sunlight and constant rains, typically requiring watering in drier areas. Sugar cane has a longer growing cycle, generally lasting 12 to 24 months. These distinctions in growing conditions substantially influence the geographical circulation and farming practices linked with each plant.
Gathering Techniques Distinctions
The harvesting techniques for sugar beet and sugar cane reflect their distinctive development attributes and agricultural methods. Sugar beet is generally collected mechanically, with harvesters designed to uproot the entire plant, making sure minimal dirt disruption. The beets are after that transferred for handling soon after harvest to maintain top quality. In contrast, sugar cane harvesting usually entails a mix of manual and mechanical approaches. Employees might initially reduce the cane by hand, especially in regions where mechanization is less viable. Ultimately, specialized equipment is used to collect and transport the cut stalks to refining facilities. These varying techniques not only effect efficiency but also influence the high quality and yield of the final sugar products, showcasing the adaptability of each crop to its setting.
Nutritional Contrast and Health Conveniences
When contrasting the dietary profiles of sugar beet and sugar cane, it ends up being clear that each offers distinctive health and wellness advantages. Sugar beetroots are abundant in essential nutrients like folate, manganese, and potassium, which contribute to total wellness. They additionally contain fiber, which aids digestion and might aid control blood sugar levels. Additionally, sugar beetroots are known for their antioxidant buildings, which can deal with oxidative anxiety.
On the other hand, sugar cane is mainly made up of sucrose, providing fast energy. While it lacks the same degree of minerals and vitamins found in sugar beets, sugar cane does contain small amounts of B minerals and vitamins such as calcium and magnesium. In addition, sugar cane juice is commonly proclaimed for its hydrating buildings and prospective health advantages, consisting of boosted gastrointestinal wellness. Eventually, the option in between sugar beet and sugar cane might depend on individual health and wellness goals and nutritional preferences.
Taste Accounts and Culinary Uses
Taste profiles of sugar beet and sugar cane differ significantly, influencing their culinary applications (Sugar beet vs sugar cane). Sugar cane, with its normally pleasant and complex taste, is usually preferred in beverages, treats, and numerous culinary dishes. It lends an abundant, caramel-like note that improves the preference of things such as syrups, molasses, and rum. On the other hand, sugar beet has a much more neutral and less fragrant preference, making it ideal for applications where sweetness is preferred without changing the recipe's intrinsic tastes. It is regularly utilized in processed foods, baked items, and sugar
Cooking specialists often choose sugar cane for its deepness and richness, specifically in premium food preparation and craft drinks. Conversely, sugar beet's versatility as a sweetener in mass-produced things caters to a more comprehensive market. Inevitably, the choice in between these two sugars can considerably impact taste accounts and general culinary experiences.
Ecological Effect of Sugar Manufacturing
Sugar manufacturing, whether from sugar beet or sugar cane, carries considerable ecological ramifications. click over here Sugar cane cultivation commonly results in logging, especially in exotic regions, disrupting regional ecological communities and adding to biodiversity loss. The considerable use of plant foods and chemicals in both sugar beet and sugar cane farming can lead to dirt destruction and water pollution, affecting surrounding environments and neighborhoods. In addition, the high water consumption needed for sugar cane watering presents a threat to regional water supplies, particularly in arid areas.
On the other hand, sugar beet farming usually occurs in pleasant environments, which may minimize some logging problems. It is not without its own difficulties, including soil erosion and reliance on chemical inputs. On the whole, the ecological influence of sugar production is complex, necessitating sustainable why not try this out farming practices and awareness of source management to reduce damage to ecosystems and promote environmental health and wellness.
Handling Strategies: From Plant to Sugar
Various handling techniques are used to transform sugar beet and sugar cane into granulated sugar, each technique mirroring the one-of-a-kind qualities of the source plant. For sugar beetroots, the process starts with cleaning and slicing the roots right into slim strips, which are after that subjected to diffusion-- a technique where warm water removes sugar from the beet pieces. The resulting liquid is purified, focused, and crystallized.
In contrast, sugar cane handling entails squashing the stalks to draw out juice, adhered to by information to get rid of impurities. The juice is after that vaporized, causing syrup that undertakes formation. Both processes are adhered to by splitting up of the sugar crystals from the molasses, which is a byproduct. The lasts include drying and packaging the granulated sugar for distribution. These strategies highlight the unique pathways whereby these two plants generate sugar, each with its own set of difficulties and efficiencies.
Economic Elements of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Industries
The financial landscape of the sugar beet and sugar cane industries exposes significant differences in manufacturing expenses, market characteristics, and local influences. Sugar beet, primarily expanded in temperate environments, often sustains higher production costs as a result of labor and input expenditures. Alternatively, sugar cane thrives in site exotic regions, typically profiting from lower labor prices and favorable weather problems, which can cause higher yields.
Market dynamics additionally differ, as sugar cane dominates worldwide manufacturing, representing roughly 80% of sugar result. This occurrence affects rates structures and profession circulations. On the other hand, sugar beet is a lot more regionally focused, specifically in Europe and North America, affecting local economies based on beet production.
Fluctuations in worldwide sugar costs can significantly impact both sectors, influencing farmer revenue and financial investment degrees. Understanding these economic elements is vital for stakeholders aiming to navigate the complexities of the sugar market effectively.
Frequently Asked Inquiries

Can Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Be Intercropped Effectively?
Intercropping sugar beet and sugar cane presents obstacles as a result of varying growth needs and ecological needs. Nonetheless, with mindful administration and suitable problems, it might generate advantages such as improved dirt wellness and resource efficiency.
What Are the Historical Beginnings of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
The historic origins of sugar beet trace back to 18th century Europe, while sugar cane has origins in Southeast Asia, cultivated for hundreds of years. Both plants have significantly affected global sugar manufacturing and agriculture.
Just How Do Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Affect Soil Health?
The impacts of sugar beet and sugar cane on soil wellness vary. Sugar beet can enhance dirt structure and nutrient web content, while sugar cane might deplete nutrients otherwise handled correctly, influencing long-lasting soil fertility.
Exist Any Type Of Emerging Technologies in Sugar Manufacturing?
Arising technologies in sugar production include precision farming, advanced hereditary engineering for higher returns, and cutting-edge removal methods. These improvements intend to improve efficiency, decrease environmental impact, and boost the total sustainability of sugar production procedures.
What Are the Key Differences in Labor Demands for Both Plants?
The crucial differences in labor demands for sugar beet and sugar cane hinge on planting, harvesting, and processing. Sugar beet vs sugar cane. Sugar beet normally demands more mechanization, while sugar cane often needs a lot more manual work for collecting and processing stages